Part 2: Lowering Barriers and Building Alliances for Responsible AI
Introduction
Federated Learning (FL) offers great potential for building scalable and secure AI systems, but few organizations have fully realized it. Many talk about privacy-preserving collaboration, yet only a handful have done it successfully at scale. The biggest challenge isn’t the idea; it’s the execution. FL requires strong technical skills, reliable infrastructure, and coordination among multiple data owners. For smaller organizations or those new to AI, starting and maintaining a shared FL project can be too expensive or complex. As a result, the promise of FL – to make secure AI development accessible to everyone, remains mostly out of reach.
To bridge this gap, DSFederal developed DSFed™, a fully integrated Federated Learning Platform that automates the complex orchestration, data governance, and advanced privacy design required to make federated learning operational at scale. It enables organizations to adopt federated learning by removing the technical and operational barriers that typically make onboarding difficult. With DSFed™, joining or initiating a federated network no longer demands extensive DevOps setup or distributed system expertise. Instead, users can launch or join projects through a low-code interface that automates node registration, model synchronization, and governance compliance. This means that every institution, regardless of size or technical maturity, can take part in secure, collaborative AI development.

Beyond accessibility, DSFed™ also enables agencies and organizations to build and govern their own federated learning ecosystems. Today, an active community of institutions, hospitals, universities, and research partners is already sharing model insights and improving their models in this way. By joining DSFed™, agencies and organizations can replicate this model to create a network tailored to their mission. Participants improve models together through shared benchmarks, collective refinement, and exposure to real-world variability. New contributors can plug directly into this cycle, transforming federated learning from a static architecture into a dynamic, mission-aligned network where each organization learns not only from its own data, but from the broader community’s experience.
By bringing usability, automation, and community into one platform, DSFed™ removes much of the friction that has historically slowed federated collaboration. It is not just an implementation of FL; it is the operationalization of its promise. Built on human-centered design and proven real-world deployments, DSFed™ helps organizations move from theory to practice and turn their data into shared intelligence securely and collaboratively.
Section 1: The Current Landscape
As FL continues to gain traction, many platforms have been developed to support privacy-aware and decentralized ML. Current federated learning frameworks differ widely in their supported model types, integration pathways, communication strategies, and security mechanisms. While many have made considerable technical progress, most tools still require significant technical expertise in FL and distributed infrastructure [1]. Therefore, while the technology of FL has matured, participation and adoption has not.
FL has mostly been accessible by well-resourced institutions with dedicated ML teams and robust IT infrastructure. As noted by Fernandez et al., 2023, many smaller healthcare providers, despite holding valuable and often underrepresented data, remain excluded due to technical and operational barriers [2]. While this study focuses on clinical settings, many of its observations, particularly around infrastructure limitations and coordination barriers, are likely to apply to other areas, including those in finance, transportation, public services, and other similarly constrained sectors. For these groups, unfamiliar FL technical steps, lack of infrastructure setup, and coordination complexity can slow or even prevent adoption. Making FL more intuitive and manageable is therefore critical. A human-centered approach focused on usability and accessibility can therefore help bridge the gap between technology and implementation.
Section 2: DSFederal’s Blueprint for Building a Practical FL Ecosystem
DSFed™ delivers advanced FL capabilities in a secure, containerized environment designed for both technical and non-technical users. With a simplified interface and automated orchestration, it removes the complexity from setup and operation. Its key differentiator is a production-ready architecture that unifies and automates the entire FL pipeline, from data governance through model deployment, via a low-code experience. Its GitOps-inspired architecture automates versioning, training coordination, and node synchronization, allowing users to focus on results rather than process or infrastructure.
Developers can still configure model logic and metrics, but non-technical users, including data contributors, can participate simply by registering their data through the web interface and using built-in AutoML modules. Project managers, in turn, can monitor participant readiness and view data/model summaries with ease. Rather than framing FL as a purely technical or backend process, DSFed™ reimagines it as an intelligent, collaborative ecosystem designed to empower both engineers and decision-makers through guided workflows and clear visibility for federated AI.
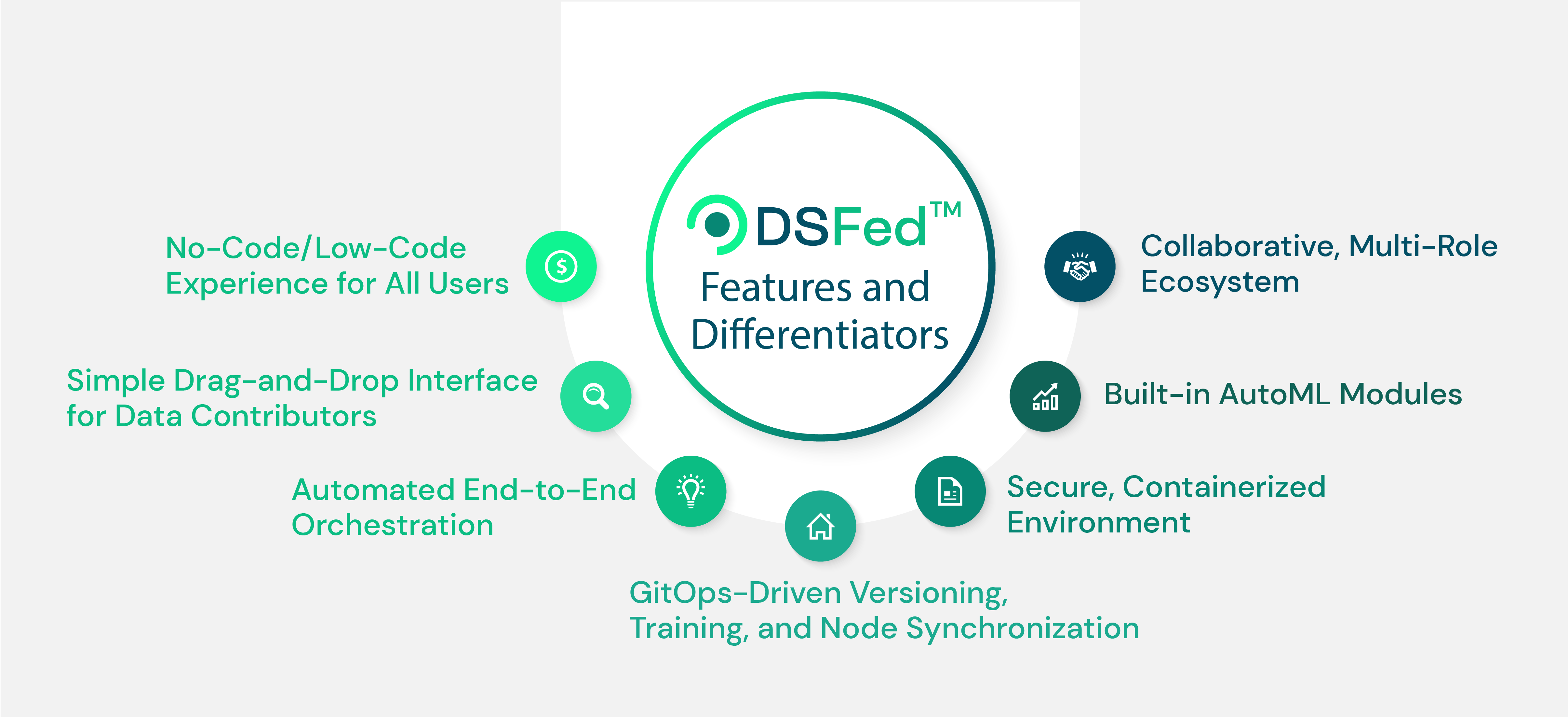
In FL, a shared understanding of data structure is essential. DSFed™ supports auto-creating, publishing and reuse of Common Data Models (CDMs), enabling participants to define a consistent schema that others in the project can readily adopt. Since data processing remain among the most resource-intensive steps in data-driven missions, standardized schema alignment in DSFed™ accelerates onboarding and minimizes integration complexity. Our solution thus has the potential to impact multiple mission areas by providing robust AI scaffolding and assuring broad data sources.
Practical FL utilization requires moving from infrastructure-only implementations to complete, ecosystem-based platforms. DSFed™ is distinguishable not just through technical capabilities, but through an already-formed alliance of active collaborators. This allows users to bring their data and insights into a shared environment where peers are readily available to co-develop and improve models, creating a living ecosystem that turns participation into shared progress in AI development. For example, in the healthcare domain, DSFed™ currently brings together more than 20 hospitals globally, alongside academic institutions and industrial partners such as MCI and NYU. The platform also supports the development of over 80 federated model training collaborations and 30 clinical trial projects across diverse health domains. This alliance-driven model offers not only accessible infrastructure, but also access to an integrated community of hospitals, researchers, and industry partners, all working toward trustworthy and scalable AI.
Section 3: A User-Friendly, End-to-End Federated Learning Experience
To make federated learning practical, accessible, and repeatable, DSFed™ turns a traditionally complex process into a four-step workflow that is easy to configure, manage, and monitor. Agencies can see exactly how projects progress through setup, participation, training, and governance. The accompanying interface screenshots show how DSFed brings these stages together in a clean, accessible user experience.
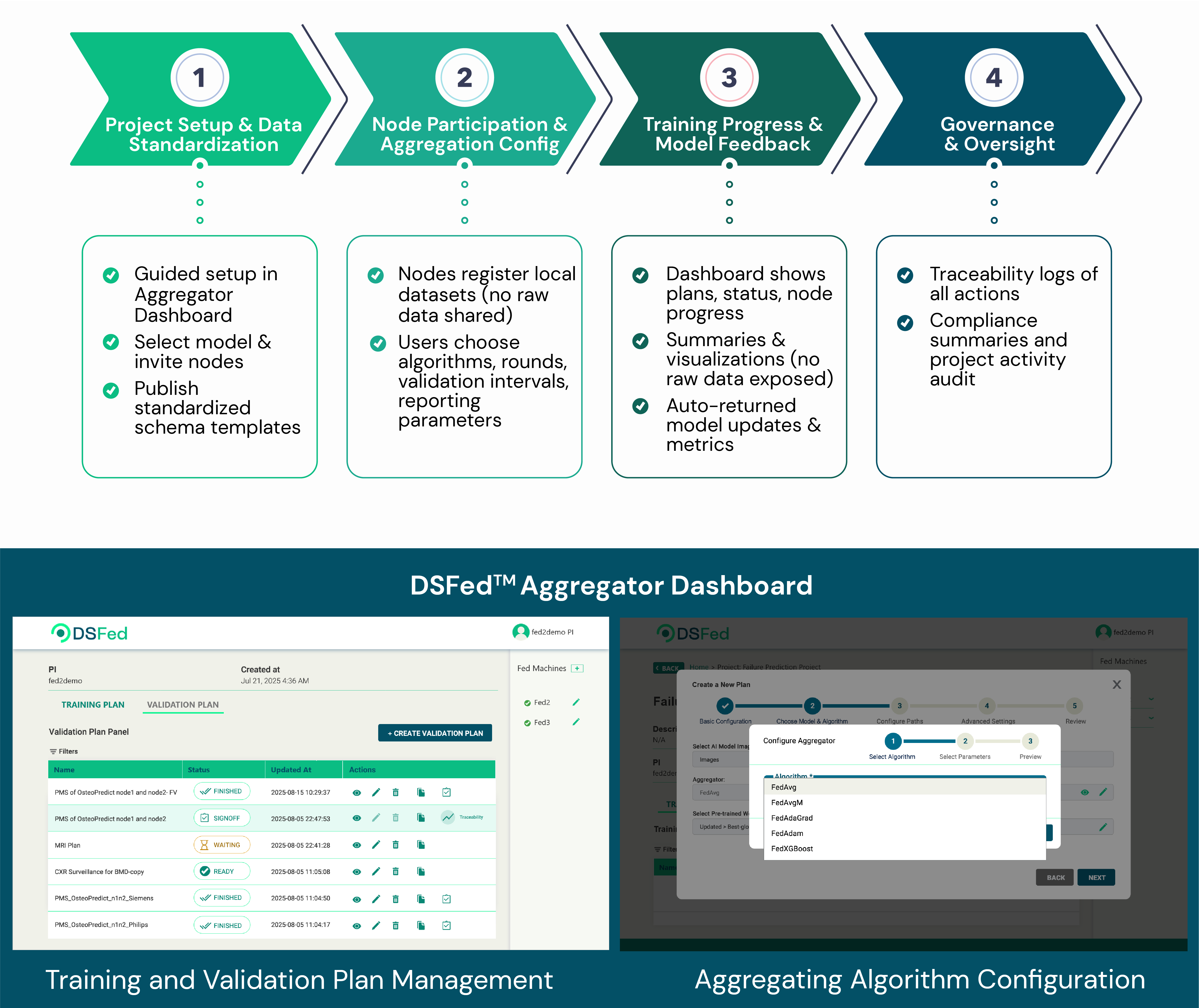
Conclusion
AI innovation is only meaningful when models are trained on real-world, heterogeneous data that remains secure and governed. DSFed™ makes this possible by providing an operational framework that maximizes outreach with simplified setup, enables privacy-preserving collaboration, and connects participants through an established alliance network. By operationalizing FL across secure, distributed environments, DSFed™ bridges the gap between data protection and data utility, allowing AI models to evolve with real-world evidence and institutional trust. DSFederal looks forward to deepening the conversation on how FL can enable more responsible data use and improve service delivery. In the next part, we will explore how FL can drive equitable AI deployment across critical sectors, and what it will take to translate technical capabilities into meaningful, real-world impact.
Contributors
Chia-yun Chang, Data Scientist Lead – Author
Shijia Huang, Data Scientist – Author
Deborah Chung, Sr. Portfolio Program Manager – Reviewer
Sehba Wani, Associate AI Engineer – Reviewer
Tracy Chong, Director of Communications – Reviewer, Graphics
References
1. Riedel, P. et al. Comparative analysis of open-source federated learning frameworks – a literature-based survey and review. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Cybern. (2024)
2. Fernandez, J. D., Brennecke, M., Barbereau, T., Rieger, A. & Fridgen, G. Federated learning: Organizational opportunities, challenges, and adoption strategies. arXiv [cs.CY] (2023).


